GitHub OAuth
Use GitHub OAuth for authenticating to Tinyauth.
Tinyauth has built-in support for GitHub OAuth with just two environment variables. Most of the configuration happens on the GitHub side rather than Tinyauth.
Requirements
- A domain name (non-gTLDs are supported)
- A GitHub account
Creating the GitHub OAuth App
Begin by creating a GitHub OAuth app. Navigate to the GitHub developer settings and click New OAuth App. Fill in the following details:
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Application name | Can be anything, e.g., Tinyauth. |
| Homepage URL | Can be any URL, e.g., https://tinyauth.app. |
| Authorization Callback URL | Enter the domain followed by /api/oauth/callback/github, e.g., https://tinyauth.example.com/api/oauth/callback/github. |
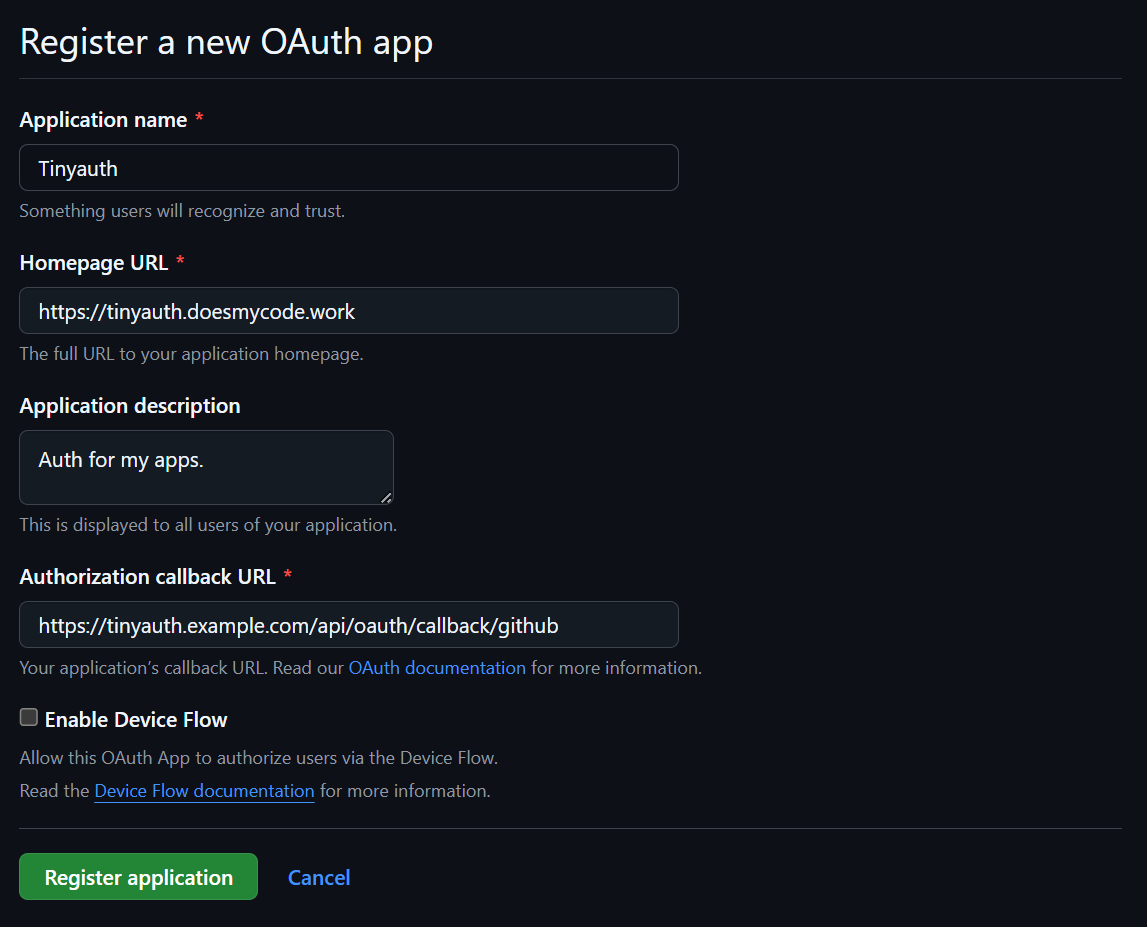
After entering the details, click Register Application.
Retrieving Credentials
Once the application is created, the following screen will appear:
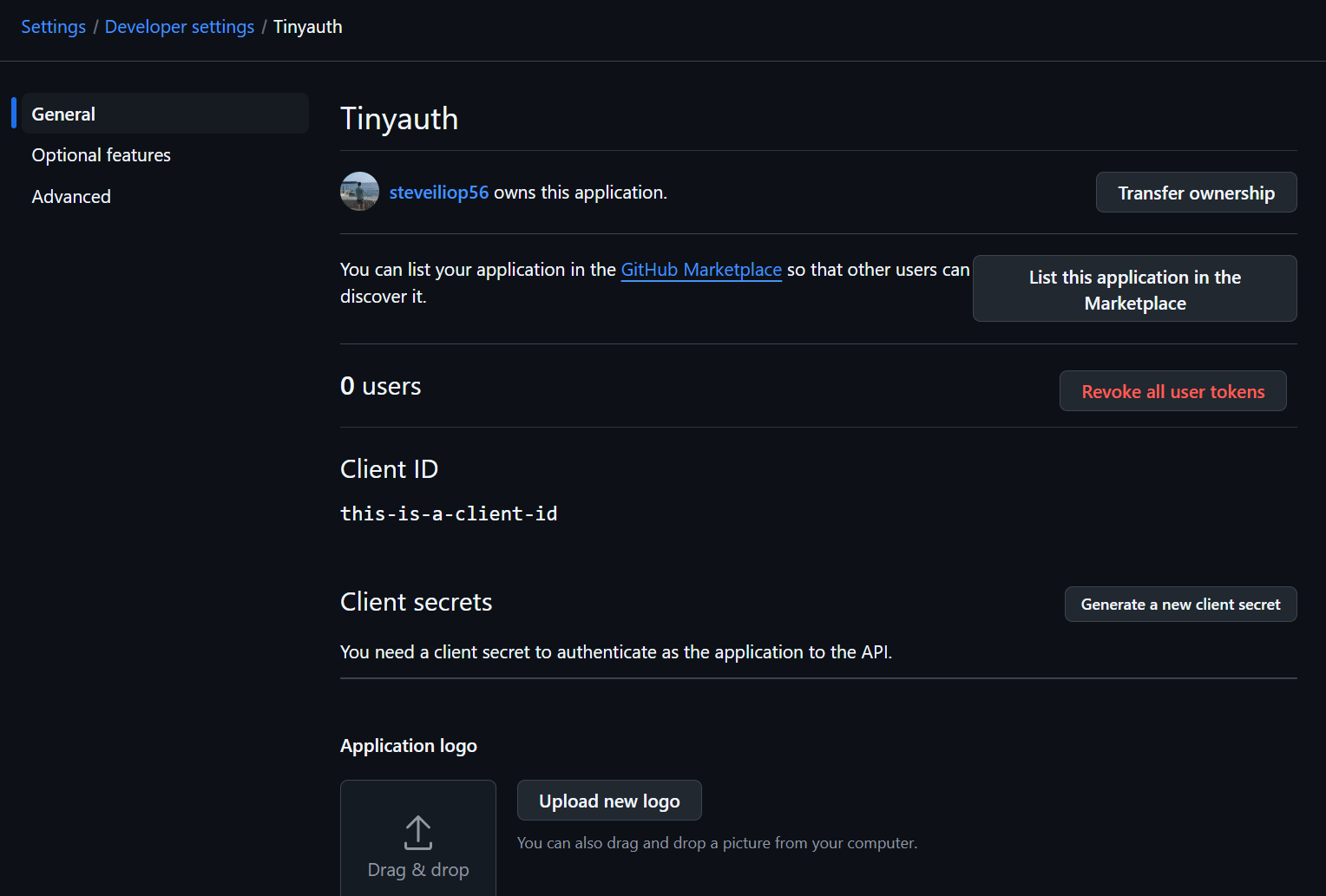
Note down the client ID. To generate the client secret, click Generate a new client secret. GitHub will prompt for login confirmation and then display the secret:
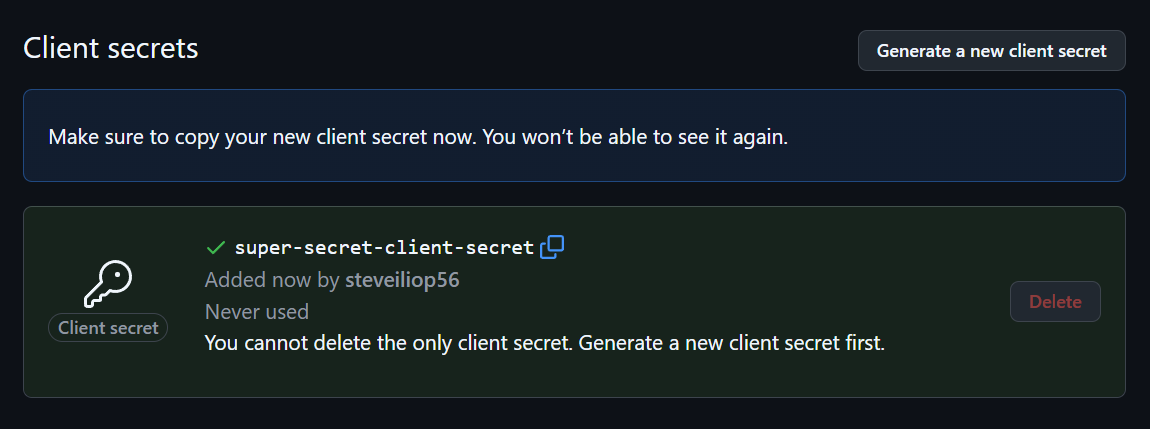
Note down the client ID and secret for later use.
Configuring Tinyauth
Add the following environment variables to the Tinyauth Docker container:
services:
tinyauth:
environment:
- PROVIDERS_GITHUB_CLIENT_ID=your-github-client-id
- PROVIDERS_GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRET=your-github-secretOAuth alone does not guarantee security. By default, any GitHub account can
log in as a normal user. To restrict access, use the OAUTH_WHITELIST
environment variable to allow specific email addresses. Refer to the
configuration page for details.
With OAuth enabled, the USERS or USERS_FILE environment variables can be
removed to allow login exclusively through the OAuth provider.
Restart Tinyauth. Upon visiting the login screen, an additional option to log in with GitHub will appear.