GitHub Apps OAuth
Use the GitHub Apps OAuth screen for authenticating to Tinyauth.
Tinyauth also supports GitHub Apps for authentication instead of OAuth Apps. GitHub Apps allow more control over permissions and are slightly more complex to set up. For simpler setups, the OAuth Apps guide is recommended.
Requirements
GitHub requires the following to set up an app:
- A domain name (non-gTLDs are supported)
- A GitHub account
Creating the GitHub App
Open the GitHub Apps site and click New GitHub App. The following screen will appear:
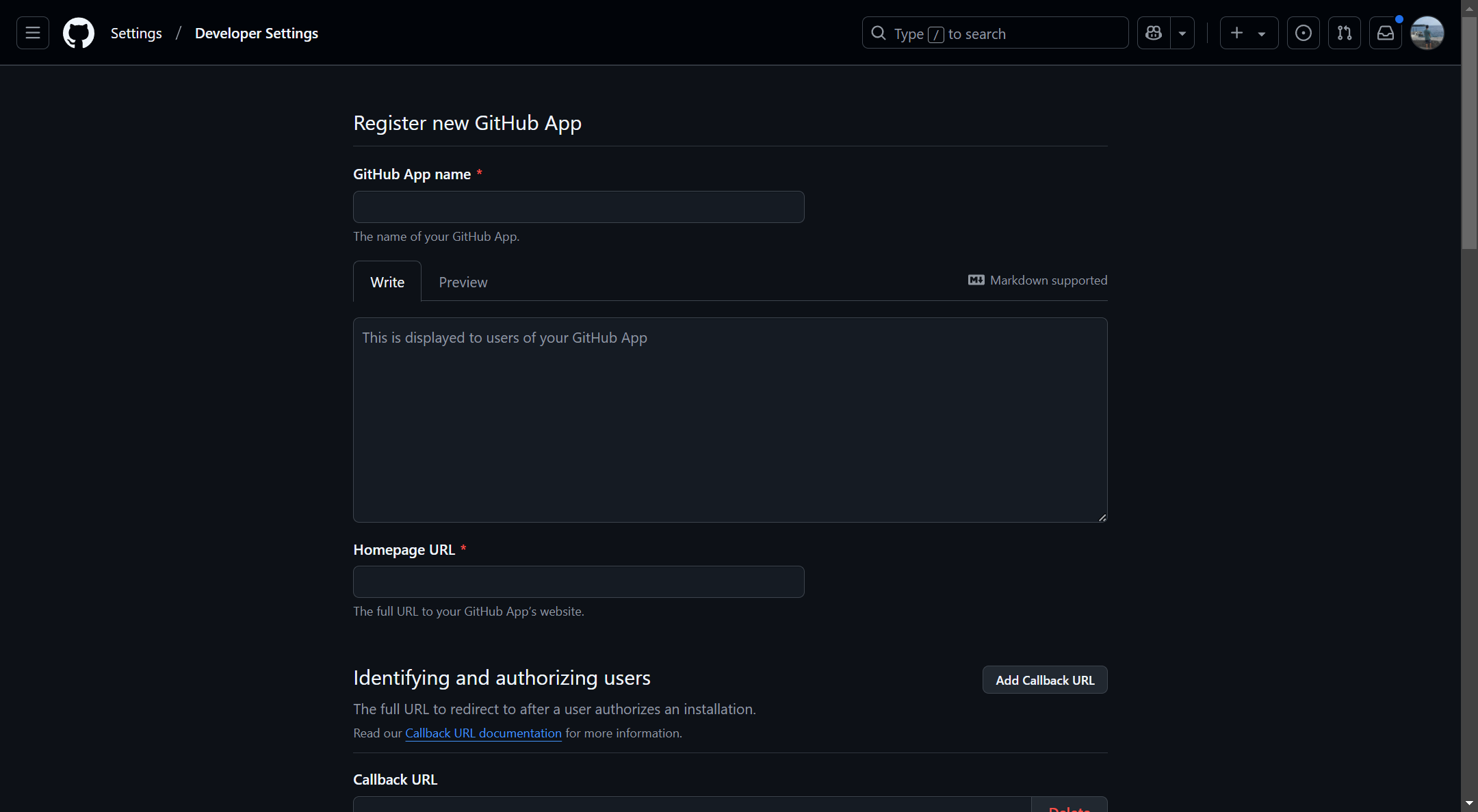
Fill in the following information:
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
| GitHub App Name | The name for the app, e.g., Tinyauth. |
| Homepage URL | Any URL, e.g., https://tinyauth.app. |
| Callback URL | The Tinyauth app URL followed by /api/oauth/callback/github, e.g., https://tinyauth.example.com/api/oauth/callback/github. |
Under webhook, ensure the Active checkbox is unchecked as webhooks are not required.
In the Permissions section, click Account permissions and set the Email Addresses option to Read-only:
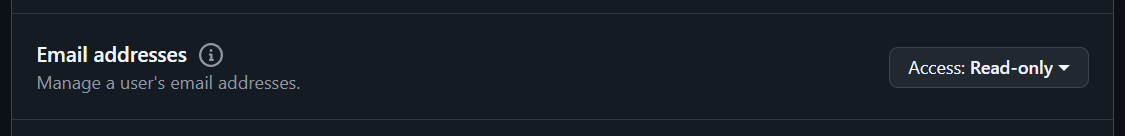
Create the app. The following screen will appear:
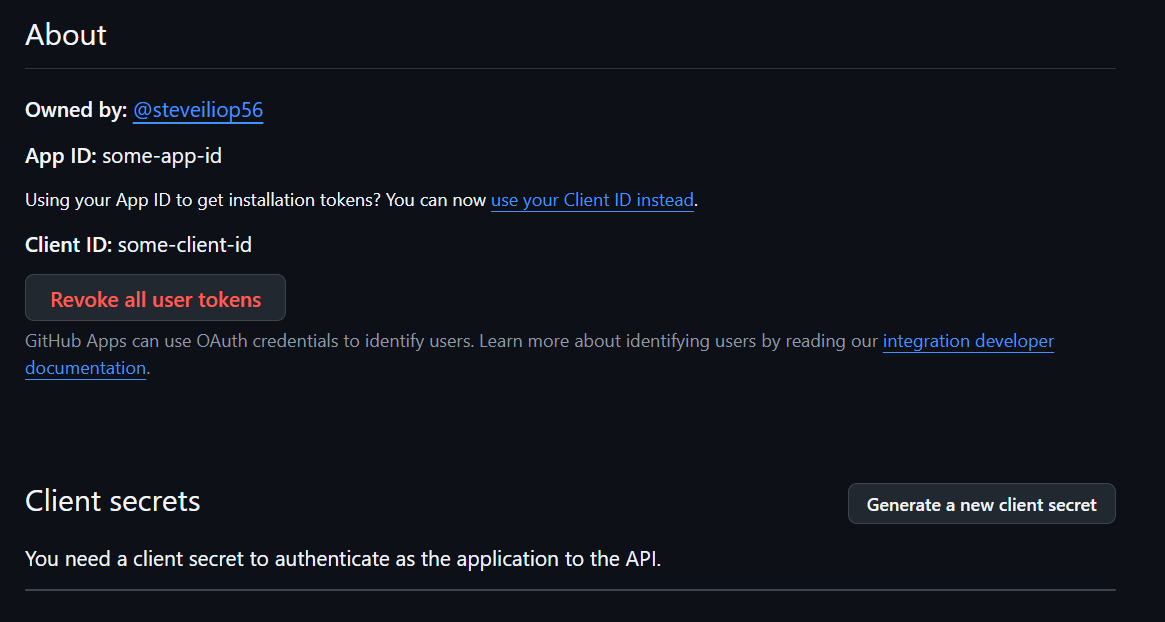
Note the client ID. To generate the client secret, click Generate new client secret. After authentication, the secret will appear:
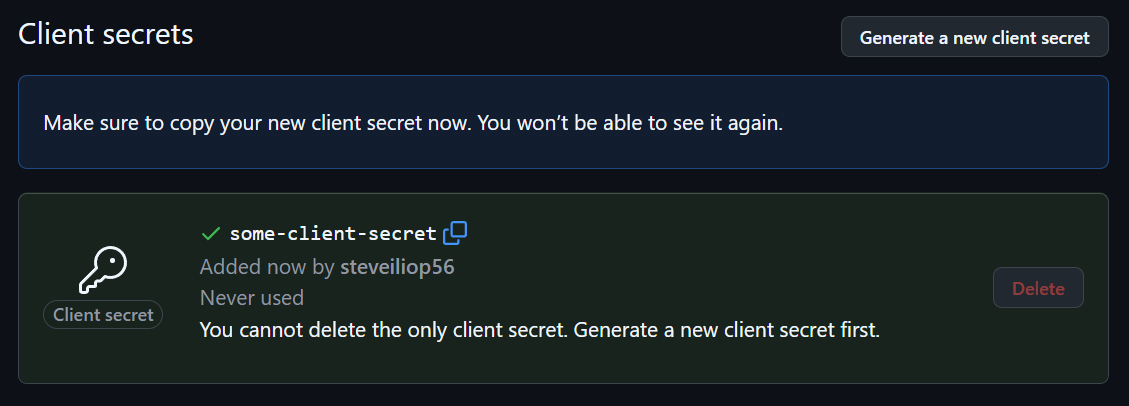
Note down the client ID and secret as they will be required for Tinyauth.
Configuring Tinyauth
Add the following environment variables to the Tinyauth Docker container:
services:
tinyauth:
environment:
- PROVIDERS_GITHUB_CLIENT_ID=your-github-client-id
- PROVIDERS_GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRET=your-github-secretOAuth alone does not guarantee security. By default, any GitHub account can
log in as a normal user. To restrict access, use the OAUTH_WHITELIST
environment variable to allow specific email addresses. Refer to the
configuration page for details.
With OAuth enabled, the USERS or USERS_FILE environment variables can be
removed to allow login exclusively through the OAuth provider.
Restart Tinyauth. Upon visiting the login screen, an additional option to log in with GitHub will appear.